

With a population of 1.4 billion people, China is the world's most populous country.The country’s culture stretches back nearly 4,000 years, but China has only recently become a “modern” nation. Today, China is experiencing rapid economic development and urbanization, leading to increased opportunity, as well as rising inequality – and a whole host of challenges for China’s youngest citizens.
As more and more parents move into China's urban centers in search of economic opportunity, an increasing proportion of children are “left behind” in the countryside, in overcrowded boarding schools or with relatives unable to care for them.
Children who join their parents in the cities don't fare much better. While their parents struggle to make ends meet, vulnerable children must often fend for themselves. In rapidly changing, modern China, childhood remains under threat.
Despite country-wide statistics, many children in China face critical threats to childhood – especially those “left behind” in remote, rural areas, including ethnic minorities, as well as those forced to fend for themselves in poor,urban ones.
|
|
Last year, thanks to supporters like you, we changed the lives of over 3,000 children in China, with a focus on the most vulnerable.

|
|
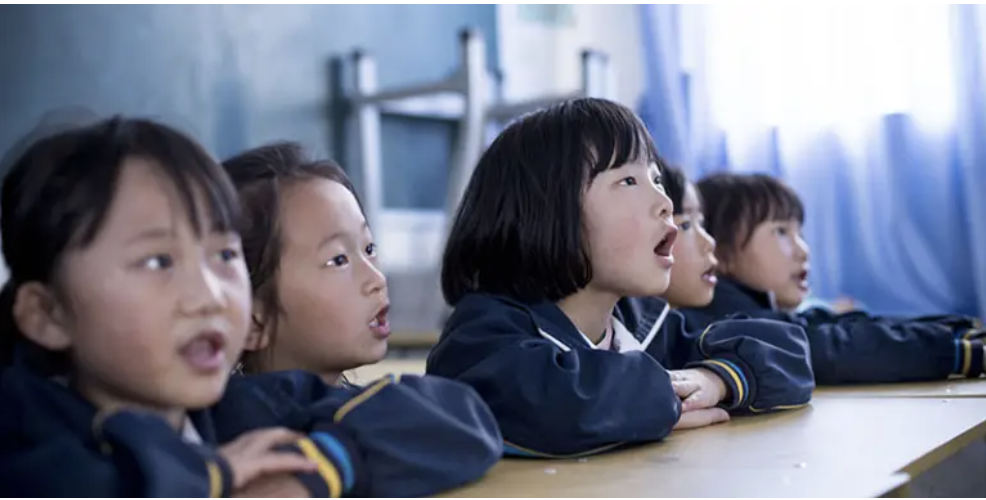
| Thanks to your support, Save the Children is working to improve basic education in rural China, where often-profoundly distressed children are “left behind” at overcrowded boarding schools while their parents pursue work in cities. |